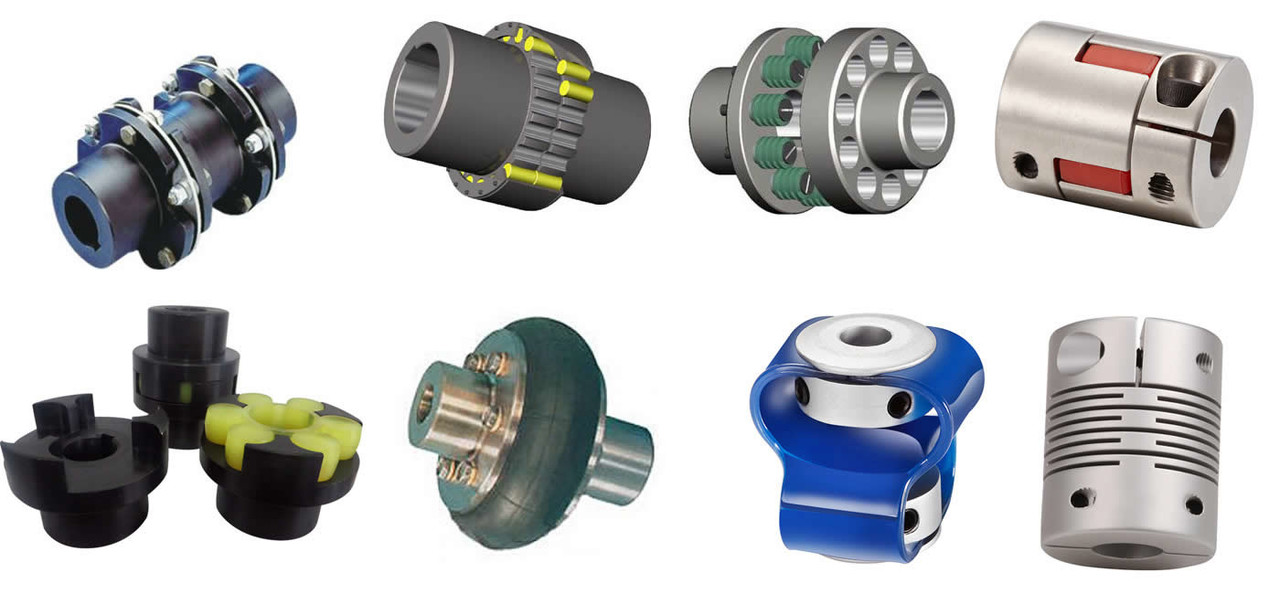
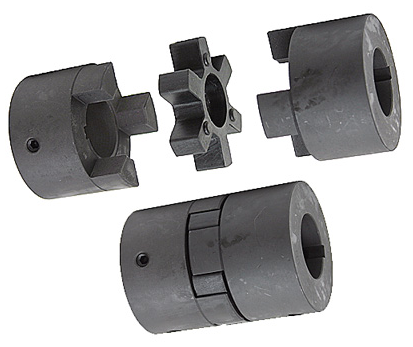
Product Description
Product Description
| Bellows couplings are used where precise rotation, high speeds, and dynamic motion must be transmitted. They exhibit zero backlash and a high level of torsional stiffness, offering distinct performance advantages. |
Product Parameters
Company Profile
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co., Ltd. specializes in manufacturing mechanical power transmission components. We Mighty is the branch of SCMC Group, a wholly state-owned company, established in 1980.
About us:
-3 manufacturing factories
We have 5 technical staff, our FTY have strong capacity for design and process design, and more than 70 workers and double shift eveyday.
-Large quality of material purchase and stock
We ensure both the quality and low cost for material and production.
-Strick quality control
We have strict process inspection and final production inspection to ensure the perfect quality.
-20 years of machinery experience
MIGHTY’s products are mainly exported to Europe, America and the Middle East market. With the top-ranking management, professional technical support and abundant export experience, MIGHTY has established lasting and stable business partnership with many world famous companies and has gained good reputation from CHINAMFG customers.
FAQ
Q: Are you manufacturer or trading company?
A: We are factory of 20+ years and also do exporting business.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 4-6 days if the goods are in stock or 15-20 days with short stock based on the quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? Is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer free sample but do not conclude the shipping cost.
Q: Do you support OEM/ODM?
A: Yes we do.
Q: Do you offer other types of shaft couplings?
A: Yes we offer a wide range of flexible and rigid couplings.
If you have another question, pls feel free to contact me without hesitation as below:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft Couplings
Shaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview:
Torque Transmission:
The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material.
When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment.
Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them.
- Parallel Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement.
- Radial Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel.
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
Flexible Couplings:
Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings.
Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical.
Torsional Stiffness:
Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash.
By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems.
“`
How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft Coupling
Regular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for:
1. Visible Damage:
Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload.
2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point.
3. Increased Temperature:
If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues.
4. Shaft Misalignment:
Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components.
5. Excessive Backlash:
If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components.
6. Lubrication Issues:
Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear.
7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:
If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation.
8. Bolts and Fasteners:
Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
9. Age and Service Life:
Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure.
10. Abnormal Performance:
Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely.
“`
Can a Damaged Shaft Coupling Lead to Equipment Failure and Downtime?
Yes, a damaged shaft coupling can lead to equipment failure and downtime in mechanical power transmission systems. Shaft couplings play a critical role in connecting rotating shafts and transmitting power between them. When a coupling becomes damaged or fails to function properly, several negative consequences can arise:
1. Misalignment Issues:
A damaged coupling may no longer be able to compensate for misalignments between the connected shafts. Misalignment can cause excessive vibration, increased wear, and premature failure of bearings and other connected components. Over time, these issues can lead to equipment breakdown and unplanned downtime.
2. Vibration and Shock Loads:
Without the damping properties of a functional coupling, vibrations and shock loads from the driven equipment can transmit directly to the driving shaft and other parts of the system. Excessive vibrations can lead to fatigue failure, cracking, and damage to the equipment, resulting in reduced operational efficiency and increased downtime.
3. Overloading and Torque Transmission:
A damaged coupling may not effectively transmit the required torque between the driving and driven shafts. In applications where the coupling is a safety device (e.g., shear pin couplings), failure to disengage during overloading situations can lead to equipment overload and damage.
4. Increased Wear and Tear:
A damaged coupling can lead to increased wear on other parts of the system. Components such as bearings, seals, and gears may experience higher stress and wear, reducing their lifespan and increasing the likelihood of breakdowns.
5. Reduced System Reliability:
A functional shaft coupling contributes to the overall reliability of the mechanical system. A damaged coupling compromises this reliability, making the system more prone to failures and unplanned maintenance.
6. Downtime and Production Loss:
When a shaft coupling fails, it often results in unscheduled downtime for repairs or replacement. Downtime can be costly for industries that rely on continuous production processes and can lead to production losses and missed delivery deadlines.
7. Safety Hazards:
In certain applications, such as heavy machinery or industrial equipment, a damaged coupling can create safety hazards for workers and surrounding equipment. Sudden failures or uncontrolled movements may pose risks to personnel and property.
Regular inspection, maintenance, and prompt replacement of damaged shaft couplings are essential to prevent equipment failure, minimize downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation of mechanical systems. It is crucial to address any signs of coupling wear or damage immediately to avoid potential catastrophic failures and costly disruptions to operations.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-29
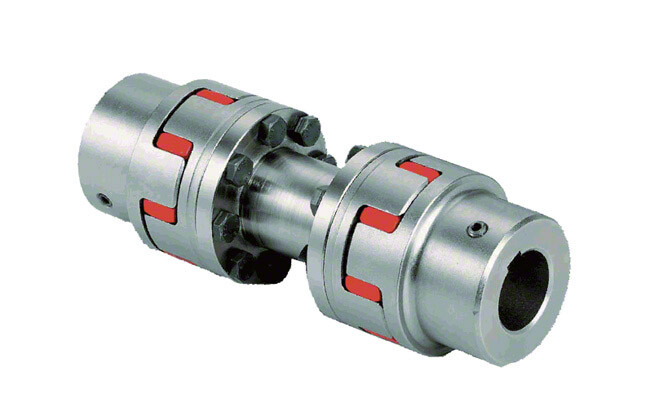
China best CHINAMFG Customized Metal Bellows Clamp Type Spring Flexible Shaft Coupling
Product Description
Densen customized Metal Bellows Clamp Type Spring flexible shaft Coupling for Step Motor
| Product Name | Metal Bellows Clamp Type Spring flexible shaft Coupling for Step Motor |
| DN mm | 12~160mm |
| Rated Torque | 25~25000 N·m |
| Allowable speed | 15300~1500 N·m |
| Material | 35CrMo/ZG270/45# steel/Aluminum alloy |
| Application | Widely used in metallurgy, mining, engineering and other fields. |
Product show
Company Information
Equipment
Application Case
Typical case of diaphragm coupling applied to variable frequency speed control equipment
JMB type coupling is applied to HangZhou Oilfield Thermal Power Plant
According to the requirements of HangZhou Electric Power Corporation, HangZhou Oilfield Thermal Power Plant should dynamically adjust the power generation according to the load of the power grid and market demand, and carry out the transformation of the frequency converter and the suction fan. The motor was originally a 1600KW, 730RPM non-frequency variable speed motor matched by HangZhou Motor Factory. The speed control mode after changing the frequency is manual control. Press the button speed to increase 10RPM or drop 10RPM. The coupling is still the original elastic decoupling coupling, and the elastic de-coupling coupling after frequency conversion is frequently damaged, which directly affects the normal power generation.
It is found through analysis that in the process of frequency conversion speed regulation, the pin of the coupling can not bear the inertia of the speed regulation process (the diameter of the fan impeller is 3.3 meters) and is cut off, which has great damage to the motor and the fan.
Later, they switched to the JMB460 double-diaphragm wheel-type coupling of our factory (patent number: ZL.99246247.9). After 1 hour of destructive experiment and more than 1 year of operation test, the equipment is running very well, and there is no Replace the diaphragm. 12 units have been rebuilt and the operation is in good condition.
Other Application Case
Spare parts
Packaging & Shipping
Contact us
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in Performance
Shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings:
1. Shaft Couplings:
Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned.
2. Gear Couplings:
Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery.
4. Disc Couplings:
Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines.
5. Jaw Couplings:
Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications.
6. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors.
7. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors.
The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system.
“`
Advantages of Using Shaft Couplings in Connecting Rotating Shafts
Shaft couplings offer several advantages in connecting rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. These advantages contribute to the efficiency, reliability, and versatility of various industrial applications. Here are the key benefits of using shaft couplings:
1. Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft couplings can accommodate different types of misalignment, including angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. This capability ensures that the connected shafts can continue to operate smoothly even if they are not perfectly aligned, reducing stress on the equipment and minimizing premature wear.
2. Vibration Damping:
Some types of shaft couplings, particularly those with flexible elements, offer vibration damping properties. They can absorb shocks and vibrations caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in operating conditions, improving the overall reliability and lifespan of the connected machinery.
3. Shock Absorption:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements can also absorb and cushion shock loads, protecting the connected components from damage and preventing system failures in high-impact situations.
4. Torque Transmission:
Shaft couplings are designed to transmit torque from one shaft to another efficiently. They ensure that the rotational motion of the driving shaft is effectively transferred to the driven shaft, allowing the equipment to perform its intended function.
5. Overload Protection:
Certain types of shaft couplings, such as shear pin couplings, act as safety devices by providing overload protection. In case of excessive torque or shock loads, the shear pin in the coupling will fail, disconnecting the driving and driven shafts and preventing damage to the equipment.
6. Angular Flexibility:
Shaft couplings with angular flexibility can handle small angular misalignments between the shafts, compensating for shaft deflection or movement due to external forces.
7. Easy Installation and Maintenance:
Shaft couplings are generally easy to install and require minimal maintenance. They are available in various designs, sizes, and materials to suit different applications and operating conditions.
8. Versatility:
Shaft couplings are versatile components used in a wide range of industries and applications. They can be found in machinery for material handling, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and more.
9. Cost-Effectiveness:
Using shaft couplings eliminates the need for rigid connections between shafts, which can be costly and difficult to implement, especially in situations where misalignment is prevalent. Shaft couplings provide a cost-effective solution for efficient power transmission.
Overall, shaft couplings play a crucial role in connecting rotating shafts, ensuring smooth power transmission, protecting equipment from misalignment-related issues, and enhancing the overall performance and reliability of mechanical systems.
“`

editor by CX 2024-02-01
China Hot selling Zs Factory Price High Precision Bellows Coupling for Automation Machinery
Product Description
Introduction
- Oldham couplings are a 3 piece design comprised of 2 aluminum hubs press fit CHINAMFG a center disk. Torque transmission is accomplished by mating the slots on the center disk to the drive tenons on the hubs. During operation the center disk slides on the tenons of each hub (which are orientated 90 apart) to transmit torque.
- While the couplings accommodate a small amount of angular and axial misalignment, they are especially useful in applications with parallel misalignment.
- We offers oldham couplings in set screw or clamp styles with bores ranging from 4mm to 35mm. Inch and metric hubs (set screw, clamp style, keyed, or keyless) are interchangeable and can be combined into a single coupling as long as they have the same outside diameter. Oldham coupling hubs are standard in black anodized aluminum for improved lubricity, increased life, and low inertia. Hubs are also available in stainless steel CHINAMFG request for increased corrosion resistance.
Application
- Ideal for many light duty industrial and motion control applications, oldham couplings have the ability to protect more expensive machinery components.
- For example the oldham coupling acts as a torque limiter during overload. When the disk fails, it breaks cleanly and does not allow any transmission of power.
- Oldham couplings also have the advantage of electrical isolation due to the non-conductive nature of the center disk.
- This prevents electrical currents from being passed to delicate instruments which can cause inaccurate data readings or damage.
Feature
- High absorption capacity of radial misaligment
- They do not produce kinematic errors in transmission
- Elimination of loads on shaft
- Mechanical protection against excessive torque
- Replaceable disc
1. We have first-class testing equipment to detect linear guide various data parameters and control the quality of the linear guide.Whenever linear guides must first detected whether the quality is qualified and the unqualified linear guide will be eliminated directly.So we can get the trust of a large customer, and supply them for several years.
2. We have our own R & D capabilities, to help customers solve the problem of non-standard linear guides.We can also according to customer requirements change their own mark.
3. Price, our manufacture ensure that our prices across China are quite competitive.It is better for you to compare prices and quality among suppliers.But everyone knows you can not buy the highest quality products with the lowest price,but our product is the best quailty if you use equal price.
FAQ:
1. When can I get the quotation ?
We usually quote within 24 hours after we get your inquiry. If you are very urgent to get the price,please call us or tell us in your email so that we will regard your inquiry priority.
2. How can I get a sample to check your quality ?
After price confirmed,sample order is available to check our quality.
3. What is your main products ?
Linear motion systems,like lead screws, flexible coupling,Miniature linear guide rails,ball screws,linear rod shaft,ceramic bearings …etc. But also CNC machining centers and CNC machinable tooling boards.
4. Could you get a better price on your products ?
Yes,you can.We will give the best price on all of the products you need,which can help you to compete other companies in your markets.
5. What is the strength of your company ?
We have a engineer team,who have well experienced on product’s and machine designs.We can help you to solve the problems you meet.
Welcome to inquiry US!

Specific Safety Precautions When Working with Shaft Couplings
Working with shaft couplings involves handling rotating machinery and mechanical components. To ensure the safety of personnel and prevent accidents, specific safety precautions should be followed during installation, maintenance, and operation:
1. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):
Prior to any work on machinery involving couplings, implement a lockout-tagout procedure to isolate the equipment from its power source. This ensures that the machinery cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair, protecting workers from potential hazards.
2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing, when working with shaft couplings. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with moving parts.
3. Proper Training and Supervision:
Only trained and authorized personnel should work with shaft couplings. Ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and experience to handle the equipment safely. Adequate supervision may be required, especially for less-experienced personnel.
4. Inspection and Maintenance:
Regularly inspect shaft couplings and associated components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents.
5. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model. Improper use or deviation from recommended procedures may compromise safety and void warranties.
6. Avoid Overloading:
Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the coupling manufacturer. Overloading a coupling can lead to premature failure and pose safety risks to operators and nearby equipment.
7. Shaft Guards and Enclosures:
Install appropriate guards and enclosures to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts and couplings. These safety measures help reduce the risk of entanglement and injuries.
8. Zero Energy State:
Ensure that all stored energy in the equipment, such as compressed air or hydraulic pressure, is released and the equipment is in a zero energy state before starting work.
9. Avoid Loose Clothing and Jewelry:
Remove or secure loose clothing, jewelry, and other items that could get caught in moving parts.
10. Maintain a Clean Work Area:
Keep the work area clean and free from clutter to avoid tripping hazards and facilitate safe movement around the machinery.
By following these safety precautions, personnel can minimize the risks associated with working with shaft couplings and create a safer working environment for everyone involved.
“`
Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling Performance
Backlash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other.
Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings.
How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:
1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision.
2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan.
3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness.
4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components.
5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance.
Minimizing Backlash:
Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness.
When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance.
“`
Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft Couplings
Regular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems:
1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment.
Diagnosis:
Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem.
Fix:
If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed.
2. Excessive Heat:
Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading.
Fix:
Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity.
3. Shaft Movement:
If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling.
Diagnosis:
Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement.
Fix:
If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts.
4. Sheared Shear Pin:
In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage.
Fix:
Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing.
5. Coupling Wear:
Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment.
Diagnosis:
Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth.
Fix:
Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications.
Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling.
“`

editor by CX 2023-09-18
China manufacturer CNC Precision Machined Steel Coupler Coupler Steel Steel High Flexible Shaft Coupler Stainless Steel Lock Assemblies Bellows Flexible Coupling
Product Description
precision CNC machined metal components -stainless steel the
these parts made on our CNC center , we always supply OEM/ODM service . if you have similar part or products needed , please feel free to contact us .
the below is our machines and equipment list :
1. Precision CNC machining/turning parts, part process size : Width max 2700mm, Length MAX 4000mm, CNC centre qty: 2 sets
2. Tolerance: +/- 0.01mm
3. Certificate: ISO 9001 quality certificate
4. all according to client’s design
Precision CNC Machining Part , competetive quote
| available process material | carbon steel , stainless , aluminum, brass , copper , bronze , steel alloy ,Nylon ,plastic etc |
| finish treatment available | polish , zinc , hard anodizing , nickel plating , chrome plating , powder coating , phostate coating ,sanblasting |
| heat treatment available | annealing, quenching hardening, blacking,tempering ,nitriding etc |
process equipment list
| equipment | process part size | qty | model |
| gantry milling machine | 6000*2300*1600 | 1 | BX2571 |
| gantry milling machine | 3000*1200*800 | 1 | XQ2012 |
| CNC centre | 1000*600 | 1 | 1060 |
| CNC centre | 1300*700 | 1 | 1370 |
| CNC centre | 4300*2700 | 1 | 4370 |
| vertical milling machine | 1500 | 1 | X53T |
| gantry boring and milling | 1800*4000 | 1 | B**2018 |
| horizontal milling machine | 960*1200*1200 | 1 | TP *611B |
| horizontal lathe | dia300*3000 | 4 | CW6163E |
| saw machine | dia5—300 | 4 | |
| grinding machine | 1000*300 | 1 | M71304 |
| grinding macnine for outer dia | 1500*3200 | 1 | M1332B |
| gantry CNC centre | 4000*2700 | 1 | YR4571 |
| common lathe | dia20–1280,L 20–5000 | 6 | |
| common drilling machine | dia2–80 | 6 | |
| plasma cut machine | 4000*12000 | 1 | SXL-400 |
| arc welding machine | 2 | 500-2 | |
| co2 welding machine | 14 | 350 500 | |
| other common machine | commong milling ,lathe , driling and milling machine etc | ||

Is It Possible to Replace a Shaft Coupling Without Professional Assistance?
Yes, it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, especially if you have some mechanical knowledge and the necessary tools. However, the ease of replacement can vary depending on the type of coupling and the complexity of the equipment. Here are some general steps to guide you through the process:
1. Safety First:
Before starting any work, ensure that the equipment is turned off and disconnected from the power source. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to protect yourself from potential hazards.
2. Assess the Coupling Type:
Different types of couplings may have specific installation and removal methods. Identify the type of coupling you need to replace, and consult the manufacturer’s documentation or online resources for guidance.
3. Gather Tools and Materials:
Collect the necessary tools, such as wrenches, sockets, and a puller (if required), to safely remove the old coupling. Have the new coupling ready for installation, ensuring it matches the specifications of the old one.
4. Disassembly:
If your coupling is a split or clamp-style coupling, you may be able to replace it without fully disassembling the connected equipment. Otherwise, you may need to remove other components to access the coupling.
5. Remove Fasteners:
Loosen and remove any fasteners, such as set screws, that secure the old coupling to the shafts. Take care not to damage the shafts during this process.
6. Extraction:
If the old coupling is tightly fitted on the shafts, you may need to use a coupling puller or other appropriate extraction tools to safely remove it.
7. Clean and Inspect:
After removing the old coupling, clean the shaft ends and inspect them for any signs of damage or wear. Also, check for any misalignment issues that may have contributed to the old coupling’s failure.
8. Install New Coupling:
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new coupling. Apply appropriate lubrication and ensure the coupling is correctly aligned with the shafts.
9. Fasten Securely:
Tighten the fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque values to securely attach the new coupling to the shafts.
10. Test Run:
After installation, perform a test run of the equipment to ensure the new coupling operates smoothly and without issues.
While it is possible to replace a shaft coupling without professional assistance, keep in mind that some couplings and equipment may require specialized knowledge and tools for safe and proper replacement. If you are uncertain about the process or encounter any difficulties, it is advisable to seek help from a qualified professional or technician to avoid potential damage to the equipment or injury to yourself.
“`
Do Shaft Couplings Require Regular Maintenance, and if so, What Does it Involve?
Yes, shaft couplings do require regular maintenance to ensure their optimal performance, extend their service life, and prevent unexpected failures. The maintenance frequency may vary based on factors such as the coupling type, application, operating conditions, and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Here’s what regular maintenance for shaft couplings typically involves:
1. Visual Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check for cracks, corrosion, and worn-out elastomeric elements (if applicable). Look for any abnormal movement or rubbing between the coupling components during operation.
2. Lubrication:
If the shaft coupling requires lubrication, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the appropriate lubricant type and frequency. Lubrication helps reduce friction, wear, and noise in the coupling.
3. Alignment Check:
Monitor shaft alignment periodically. Misalignment can lead to premature coupling failure and damage to connected equipment. Make adjustments as needed to keep the shafts properly aligned.
4. Torque Check:
For bolted couplings, periodically check the torque on the bolts to ensure they remain securely fastened. Loose bolts can lead to misalignment and reduce coupling performance.
5. Replace Worn Components:
If any coupling components show signs of wear or damage beyond acceptable limits, replace them promptly with genuine replacement parts from the manufacturer.
6. Environmental Considerations:
In harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, take additional measures to protect the coupling, such as applying corrosion-resistant coatings or using special materials.
7. Monitoring Coupling Performance:
Implement a monitoring system to track coupling performance and detect any changes or abnormalities early on. This could include temperature monitoring, vibration analysis, or other condition monitoring techniques.
8. Professional Inspection:
Periodically have the coupling and connected machinery inspected by qualified professionals to identify any potential issues that may not be apparent during regular inspections.
By adhering to a regular maintenance schedule and taking proactive measures to address potential issues, you can ensure that your shaft couplings operate reliably and efficiently throughout their service life, minimizing downtime and improving overall system performance.
“`
What is a Shaft Coupling and Its Role in Mechanical Power Transmission?
A shaft coupling is a mechanical device used to connect two shafts together at their ends, allowing for the transmission of mechanical power from one shaft to another. It serves as an essential component in various machinery and industrial applications where rotational motion needs to be transmitted between two shafts that are not perfectly aligned or are separated by a distance.
The role of a shaft coupling in mechanical power transmission includes the following:
1. Power Transmission:
The primary function of a shaft coupling is to transmit power from a driving shaft to a driven shaft. When the driving shaft rotates, the coupling transfers the rotational motion to the driven shaft, enabling the driven equipment to perform its intended function.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
In real-world applications, it is often challenging to achieve perfect alignment between two shafts due to manufacturing tolerances or dynamic conditions. Shaft couplings are designed to accommodate different types of misalignment, such as angular, parallel, and axial misalignment, allowing the equipment to function smoothly even when the shafts are not perfectly aligned.
3. Vibration Damping:
Shaft couplings can help dampen vibrations and shocks caused by uneven loads or sudden changes in the operating conditions. This vibration damping feature protects the connected components from damage and contributes to the overall system’s reliability.
4. Overload Protection:
In some cases, a shaft coupling can act as a safety device by providing overload protection. When the connected machinery experiences excessive torque or shock loads, certain types of couplings can disengage or shear to prevent damage to the equipment.
5. Torque and Speed Conversion:
Shaft couplings can be designed to provide torque and speed conversion between the driving and driven shafts. This allows for adaptation to different operating conditions and varying torque requirements in the connected machinery.
6. Flexible Connection:
Shaft couplings with flexible elements, such as elastomeric inserts or flexible discs, provide a flexible connection that can absorb shocks and misalignments. This flexibility helps reduce stress on the connected equipment and extends its lifespan.
Overall, shaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, enabling the efficient transfer of rotational motion between shafts while accommodating misalignments and providing protection against overloads and vibrations. The selection of the appropriate coupling type and design depends on the specific requirements of the application, including the type of misalignment, torque capacity, and operating conditions.
“`

editor by CX 2023-08-21