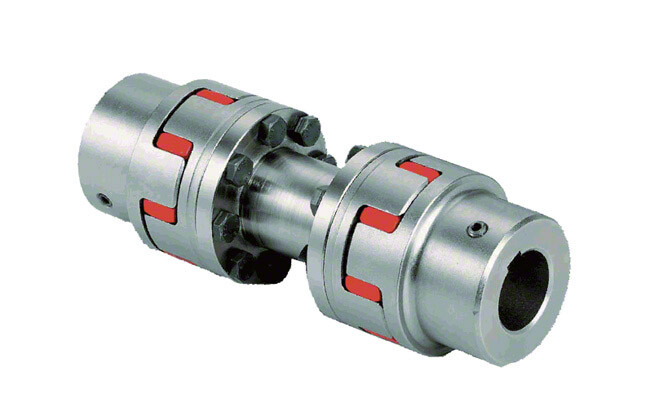
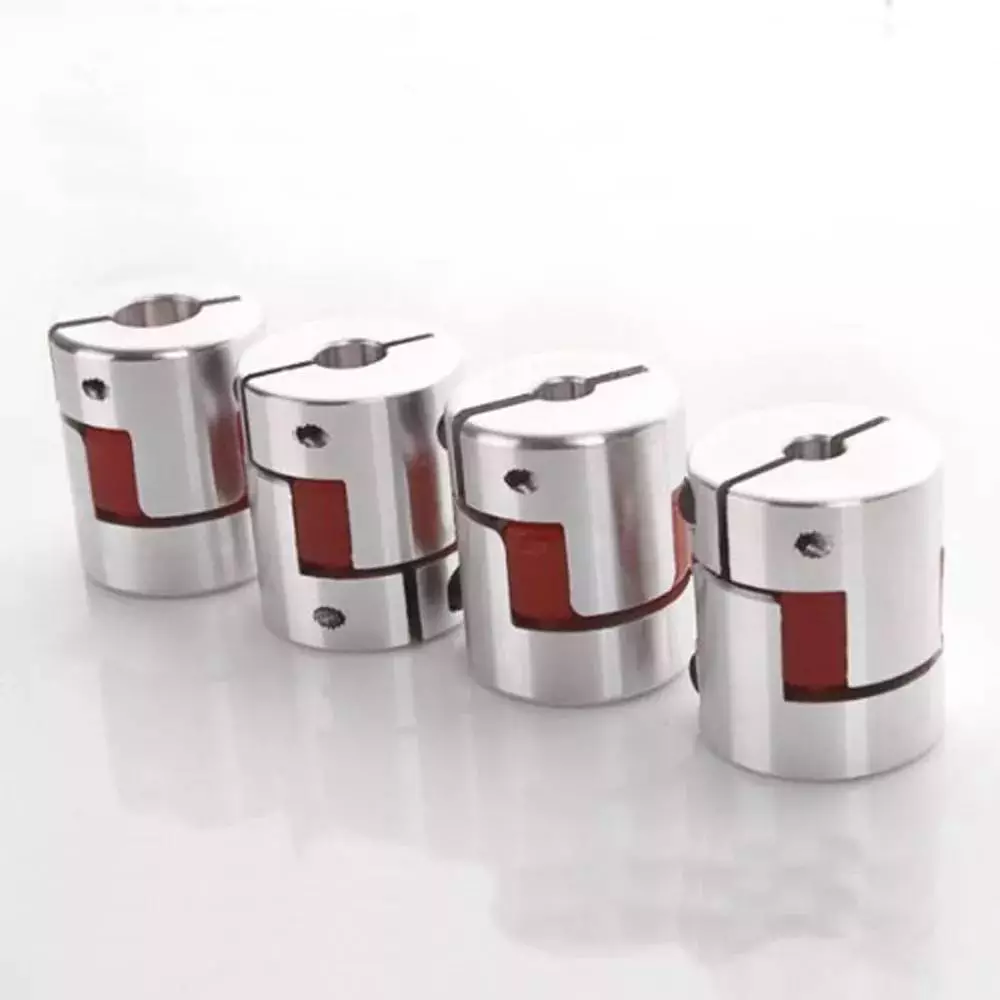
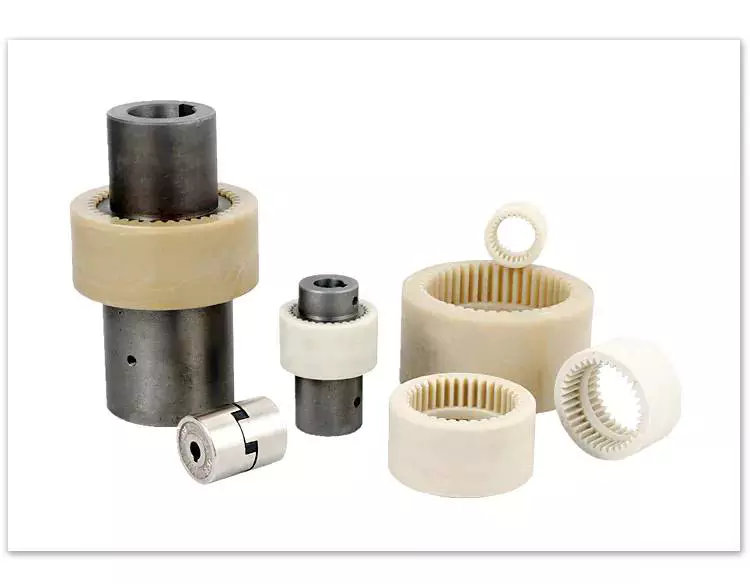
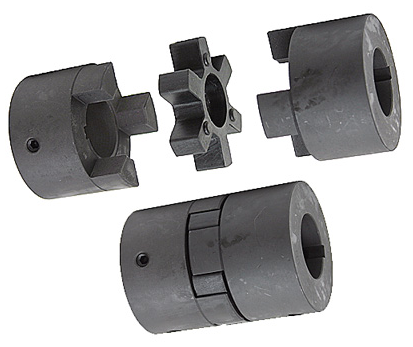
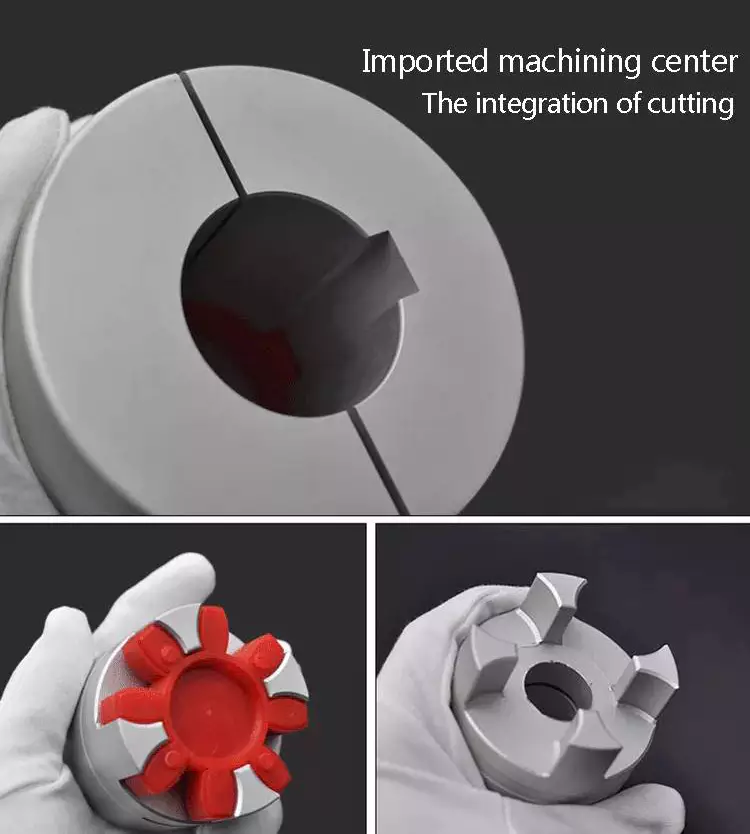
Product Description
Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint Coupling
Product Description
Main products
Coupling refers to a device that connects 2 shafts or shafts and rotating parts, rotates together during the transmission of motion and power, and does not disengage under normal conditions. Sometimes it is also used as a safety device to prevent the connected parts from bearing excessive load, which plays the role of overload protection.
Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings.
Rigid couplings do not have buffering property and the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes. It is required that the 2 axes be strictly aligned. However, such couplings are simple in structure, low in manufacturing cost, convenient in assembly and disassembly, and maintenance, which can ensure that the 2 axes are relatively neutral, have large transmission torque, and are widely used. Commonly used are flange coupling, sleeve coupling and jacket coupling.
Flexible coupling can also be divided into flexible coupling without elastic element and flexible coupling with elastic element. The former type only has the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes, but cannot cushion and reduce vibration. Common types include slider coupling, gear coupling, universal coupling and chain coupling; The latter type contains elastic elements. In addition to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 axes, it also has the functions of buffering and vibration reduction. However, due to the strength of elastic elements, the transmitted torque is generally inferior to that of flexible couplings without elastic elements. Common types include elastic sleeve pin couplings, elastic pin couplings, quincunx couplings, tire type couplings, serpentine spring couplings, spring couplings, etc
Coupling performance
1) Mobility. The movability of the coupling refers to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 rotating components. Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all put CHINAMFG requirements for mobility. The movable performance compensates or alleviates the additional load between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components caused by the relative displacement between rotating components.
(2) Buffering. For the occasions where the load is often started or the working load changes, the coupling shall be equipped with elastic elements that play the role of cushioning and vibration reduction to protect the prime mover and the working machine from little or no damage.
(3) Safe, reliable, with sufficient strength and service life.
(4) Simple structure, easy to assemble, disassemble and maintain.
How to select the appropriate coupling type
The following items should be considered when selecting the coupling type.
1. The size and nature of the required transmission torque, the requirements for buffering and damping functions, and whether resonance may occur.
2. The relative displacement of the axes of the 2 shafts is caused by manufacturing and assembly errors, shaft load and thermal expansion deformation, and relative movement between components.
3. Permissible overall dimensions and installation methods, and necessary operating space for assembly, adjustment and maintenance. For large couplings, they should be able to be disassembled without axial movement of the shaft.
In addition, the working environment, service life, lubrication, sealing, economy and other conditions should also be considered, and a suitable coupling type should be selected by referring to the characteristics of various couplings.
If you cannot determine the type, you can contact our professional engineer
Related products
Company Profile
Our Equipments
Main production equipment:
Large lathe, surface grinder, milling machine, gear shaper, spline milling machine, horizontal broaching machine, gear hobbing machine, shaper, slotting machine, bench drilling machine, radial drilling machine, boring machine, band sawing machine, horizontal lathe, end milling machine, crankshaft grinder, CNC milling machine, casting equipment, etc.
Inspection equipment:
Dynamic balance tester, high-speed intelligent carbon and sulfur analyzer, Blochon optical hardness tester, Leeb hardness tester, magnetic yoke flaw detector, special detection, modular fixture (self-made), etc.
Machining equipments
Heat equipment
Our Factory
Application – Photos from our partner customers
Company Profile
Our leading products are mechanical transmission basic parts – couplings, mainly including universal couplings, drum gear couplings, elastic couplings and other 3 categories of more than 30 series of varieties. It is widely used in metallurgical steel rolling, wind power, hydropower, mining, engineering machinery, petrochemical, lifting, paper making, rubber, rail transit, shipbuilding and marine engineering and other industries.
Our factory takes the basic parts of national standards as the benchmark, has more than 40 years of coupling production experience, takes “scientific management, pioneering and innovation, ensuring quality and customer satisfaction” as the quality policy, and aims to continuously provide users with satisfactory products and services. The production is guided by reasonable process, and the ISO9001:2015 quality management system standard is strictly implemented. We adhere to the principle of continuous improvement and innovation of coupling products. In recent years, it has successfully developed 10 national patent products such as SWF cross shaft universal coupling, among which the double cross shaft universal joint has won the national invention patent, SWF cross shaft universal coupling has won the new product award of China’s general mechanical parts coupling industry and the ZHangZhoug Province new product science and technology project.
Our factory has strong technical force, excellent process equipment, complete professional production equipment, perfect detection means, excellent after-sales service, various products and complete specifications. At the same time, we can provide the design and manufacturing of special non-standard products according to the needs of users. Our products sell well at home and abroad, and are trusted by the majority of users. We sincerely welcome friends from all walks of life at home and abroad to visit and negotiate for common development.p
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed Requirements
Selecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling:
1. Determine Torque and Speed:
Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute).
2. Calculate Torque Capacity:
Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements.
3. Consider Misalignment:
If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications.
4. Assess Operating Speed:
For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings.
5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:
If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings.
6. Check Torsional Stiffness:
In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash.
7. Size and Space Constraints:
Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance.
8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:
Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications.
9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:
Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system.
“`
Can Shaft Couplings Handle Reversing Loads and Shock Loads Effectively?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to handle both reversing loads and shock loads effectively, but the capability depends on the specific type of coupling and its design.
Reversing Loads:
Many shaft couplings, such as elastomeric couplings, gear couplings, and grid couplings, can handle reversing loads without any issue. Reversing loads occur when the direction of the torque changes periodically, causing the shafts to rotate in opposite directions. The flexibility of elastomeric couplings and the sturdy design of gear and grid couplings allow them to accommodate these reversing loads while maintaining reliable torque transmission.
Shock Loads:
Shock loads are sudden and high-magnitude forces that occur during start-up, sudden stops, or impact events. Shaft couplings with shock-absorbing features, such as elastomeric couplings and grid couplings, excel at handling shock loads. The elastomeric material in elastomeric couplings and the grid element in grid couplings act as shock absorbers, reducing the impact on the connected equipment and minimizing the risk of damage to the coupling itself.
It’s essential to select the appropriate coupling type based on the specific application’s requirements, including the magnitude and frequency of reversing loads and shock loads. Some couplings may have limitations on the amount of shock load they can handle, so it’s crucial to refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines for proper coupling selection.
In heavy-duty applications with high reversing loads and shock loads, it may be necessary to consider specialized couplings designed explicitly for such conditions, like disc couplings or fluid couplings, which can offer even better performance in handling these challenging load conditions.
“`
How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?
Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two:
1. Flexibility:
The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts.
2. Misalignment Compensation:
Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure.
3. Damping Properties:
Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts.
4. Torque Transmission:
Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications.
5. Types of Applications:
Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment.
6. Installation:
Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear.
The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-25
China Best Sales Stainless Steel Quick Shaft Flexible Ductile Iron Grooved Steel Pipe Fitting Connector/Coupling
Product Description
Product Name: Stainless Steel Quick Shaft Flexible Ductile Iron Grooved Steel Pipe fitting Connector/Coupling
Other Product
Product Description
| Key:grooved pipe fitting,steel pipe connector,hardware,elbow,steel pipe coupling |
| Material:ductile iron/35CrMo |
| Surface Treatment:Spray or dip paint and other corrosion resistant treatment |
| Packaging:Plastic bags for internal use and wooden cases for external use |
| Shipping:FedEx,EMS,DHL,AIR or Sea |
| Payment:T/T,L/C,Money gram,Western union |
| Application:Fire,water supply,Mining pipe |
| Two pieces of shell: the color is mostly red, others need to be customized, internal processing groove, groove connection is more convenient, fast and safe. A rubber ring: the material is mostly CHINAMFG or fluorine rubber, to ensure that the internal seal does not leak. Four bolts and nuts: High strength galvanized bolts and nuts, corrosion resistance, high compressive strength. |
Detailed Photos
Our Advantages
1. Rich manufacturing experience.
2. Design ability.
We have excellent design and development staff.
3. Perfect equipment.
All kinds of production equipment more than 80 sets, professional inspection, testing equipment more than 50 sets.
4. Strict quality control.
Product manufacturing quality in accordance with ISO90001 quality management system requirements.
5. Serve customers attentively.
(1) 24-hour specially-assigned personnel to solve problems for you.
(2) High production efficiency and punctual delivery.
(3) Perfect after-sales service.
Company Profile
HangZhou Tontr Pipeline System Co., Ltd. is located in the beautiful coastal city of HangZhou. It is a professional national-level high-tech industry engaged in the design, development, manufacture and sales of high-pressure pipeline systems.
The company has passed international management system certifications. Product design and development, production process, and quality control are strictly implemented in accordance with the ISO9001 quality management system requirements; product performance meets the requirements of FM, UL, GB5135.11, GB/T8259 and other domestic and foreign standards.
The main products for long-distance liquid supply system.The main function is to transport liquids such as high-pressure emulsion and high-pressure spray to the partial opening of the working face at a high pressure, to provide power for the hydraulic support of the working face, the self-movement of the loader and the tail of the belt conveyor, etc. Provide high pressure water.
The company has solved the connection and installation of pipeline systems for many large state-owned enterprises, and has won wide acclaim from customers.
Pursuing product quality and serving customers with heart is our company’s philosophy.Hope we can cooperate with all customers who have needs for a long time.
FAQ
Q1: Are you a manufacturer?
A. Yes, we are A manufacturer, and our products have been certified by ISO and other international management systems.
Q2: What’s your delivery time?
B. Depending on the order quantity and your location, it will take about 15-30 days.
Q3: What are your payment terms?
C. We accept 30% T/T in advance and 70% during shipment or at L/C sight.
Q4: Do you provide samples?
D: If you need some samples for testing, we can make them according to your requirements. Samples will be prepared and sent by express within a week, usually arriving within 4-7 days. You need to pay for the sample and shipping fee.
Q5: Can you design and manufacture specifically for customers?
E: Of course. Our design and development personnel can design and produce products according to your needs.
Q6:Could we pay a visit to your factory?
Yes,you are always welcome to our factory.
Packing&Shipping
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
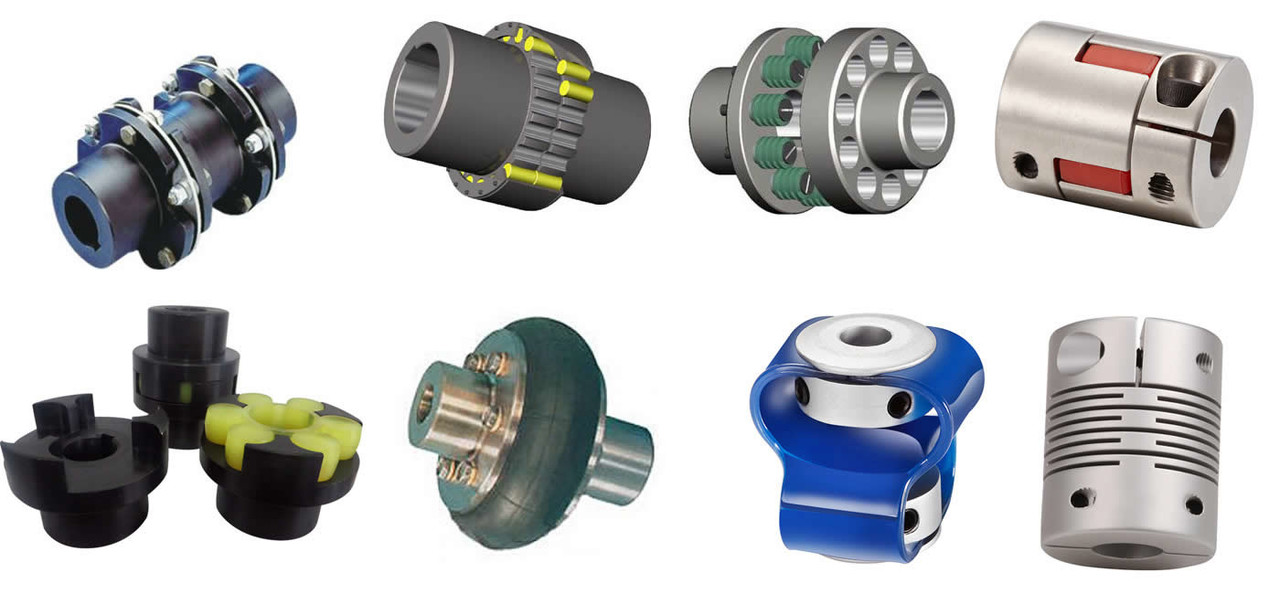

Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft Couplings
Shaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview:
Torque Transmission:
The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material.
When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment.
Misalignment Compensation:
Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency.
Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
- Angular Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them.
- Parallel Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement.
- Radial Misalignment: Occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel.
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions.
Flexible Couplings:
Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings.
Rigid Couplings:
Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical.
Torsional Stiffness:
Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash.
By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems.
“`
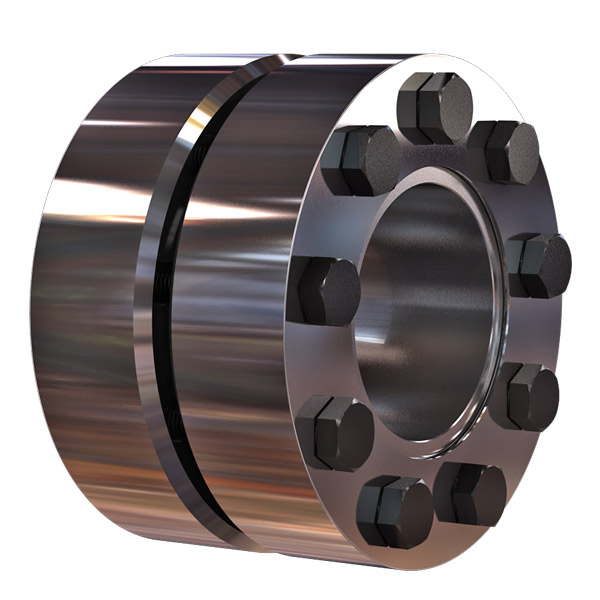
Temperature and Speed Limits for Different Shaft Coupling Types
The temperature and speed limits of shaft couplings vary depending on the materials and design of the coupling. Manufacturers provide specific guidelines and ratings for each coupling type. Below are general temperature and speed limits for some common shaft coupling types:
1. Elastomeric Couplings:
Elastomeric couplings, such as jaw couplings and tire couplings, typically have temperature limits ranging from -40°C to 100°C (-40°F to 212°F). The speed limits for elastomeric couplings are generally up to 5,000 RPM, but some designs may allow higher speeds.
2. Metallic Couplings:
Metallic couplings, like gear couplings and disc couplings, can handle a wider temperature range, typically from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for metallic couplings vary based on the size and design, but they can range from 3,000 RPM to over 10,000 RPM.
3. Grid Couplings:
Grid couplings have temperature limits similar to metallic couplings, ranging from -50°C to 200°C (-58°F to 392°F). The speed limits for grid couplings are typically in the range of 3,000 to 5,000 RPM.
4. Oldham Couplings:
Oldham couplings usually have temperature limits from -30°C to 100°C (-22°F to 212°F) and speed limits ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 RPM.
5. Beam Couplings:
Beam couplings generally have temperature limits from -40°C to 120°C (-40°F to 248°F) and speed limits between 5,000 to 10,000 RPM.
6. Fluid Couplings:
Fluid couplings are suitable for a wide range of temperatures, often from -50°C to 300°C (-58°F to 572°F). The speed limits depend on the size and design of the fluid coupling but can extend to several thousand RPM.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and the actual temperature and speed limits may vary based on the specific coupling manufacturer, material quality, and application requirements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s documentation and technical specifications for accurate and up-to-date temperature and speed limits for a particular shaft coupling model.
“`
Best Practices for Installing a Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance
Proper installation of a shaft coupling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure. Follow these best practices to install a shaft coupling correctly:
1. Shaft Alignment:
Ensure that both the driving and driven shafts are properly aligned before installing the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and other connected components, reducing efficiency and causing premature wear. Use alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve accurate shaft alignment.
2. Cleanliness:
Before installation, clean the shaft ends and the coupling bore thoroughly. Remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could interfere with the coupling’s fit or cause misalignment.
3. Lubrication:
Apply the recommended lubricant to the coupling’s contact surfaces, such as the bore and shaft ends. Proper lubrication ensures smooth installation and reduces friction during operation.
4. Correct Fit:
Ensure that the coupling is the correct size and type for the application. Use couplings with the appropriate torque and speed ratings to match the equipment’s requirements.
5. Fastening:
Use the recommended fastening methods, such as set screws or keyways, to securely attach the coupling to the shafts. Make sure the fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation.
6. Spacer or Adapter:
If required, use a spacer or adapter to properly position the coupling on the shafts and maintain the desired distance between the driving and driven components.
7. Avoid Shaft Damage:
Be careful during installation to avoid damaging the shaft ends, especially when using set screws or other fastening methods. Shaft damage can lead to stress concentrations and eventual failure.
8. Check Runout:
After installation, check the coupling’s runout using a dial indicator to ensure that it rotates smoothly and without wobbling. Excessive runout can indicate misalignment or improper fit.
9. Periodic Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling and its components for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Perform routine maintenance as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent issues from worsening over time.
10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and guidelines. Different types of couplings may have specific installation requirements that need to be adhered to for optimal performance and safety.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your shaft coupling is installed correctly, maximizing its efficiency and reliability in your mechanical power transmission system.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-24
China OEM Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centaflex
Product Description
Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centafle
Product Display:
| Model | Outer Diameter(mm) | Inner Diameter(mm) | Hight(mm) | Diameter from Hole to Hole(mm) | Weight(kg) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4A/4AS | 103 | 53 | 28 | 68 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8A/8AS | 134 | 71 | 32 | 88 | 0.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16A/16AS | 160 | 80 | 41 | 110 | 0.54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22A/22AS | 165 | 86 | 41 | 128 | 0.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25A/25AS | 183 | 102 | 46 | 123 | 0.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28A/AS | 0.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30A/30AS | 213 | 117 | 57 | 145 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50A/50AS | 220 | 123 | 57 | 165 | 1.48 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 80A/80As | 225 | 120 | 65 | 167 | 1.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 90A/90As | 278 | 148 | 70 | 190 | 3.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 140A/140AS | 285 | 151 | 71 | 215 | 3.42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 250A/250AS | 6.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 284B | 6.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4, 4655134, EX3, ZAX460MTH, ZAX480MTH, 4636444, ZX470-3, EX470, ZAX470, ZAX450-3, ZAX450-3F, ZAX5, Atlas Copco,,
AC 385, AC 396, AC415, AC416, AC 455, AC485, AC 486, AC86, AC836, AC976, AC 6-712, 4DNV98 Chinese Brand Excavators: LGK: 6085, 200 CLG 60, 205, 220, 906, 907, 908, 920, 925, 936, CLG906C, CLG922LG YC50-8, YC60-8, YC60-8, YC135-8, YC230, YC230-8, YC230LC-8, YC360, YC85, YC50, YC85-7, YC60-7, YC135 SW50, 60, 70, 150 FR85-7, FR65, FR80, FR150-7, ZL 60, 205, 230, 360 SY55, SY60, SY215, SY230, SY210, SY220, SY310 /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure. Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life. “` Comparing Shaft Couplings with Other Types of Couplings in PerformanceShaft couplings are essential components in mechanical power transmission systems, and their performance characteristics vary depending on the coupling type. Let’s compare shaft couplings with other common types of couplings: 1. Shaft Couplings:Shaft couplings come in various designs, including flexible and rigid couplings. They are widely used in a broad range of applications due to their ability to transmit torque and accommodate misalignments between rotating shafts. Flexible shaft couplings, with elastomeric or metallic elements, offer good misalignment compensation and damping characteristics. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, provide precise torque transmission and are ideal for applications where shafts are well-aligned. 2. Gear Couplings:Gear couplings are robust and designed for heavy-duty applications. They consist of two external gear hubs with internal gear teeth that mesh together. Gear couplings can handle high torque, high-speed, and angular misalignment. They are often used in demanding industries such as steel, mining, and paper manufacturing. 3. Grid Couplings:Grid couplings feature a flexible grid element between the two halves of the coupling. They provide excellent shock absorption and misalignment compensation. Grid couplings are commonly used in pumps, compressors, and other industrial machinery. 4. Disc Couplings:Disc couplings utilize flexible metallic discs to transmit torque and compensate for misalignment. They offer high torsional stiffness, making them suitable for applications requiring precise motion control, such as robotics and CNC machines. 5. Jaw Couplings:Jaw couplings consist of two hubs with elastomeric spider inserts. They are easy to install, have good misalignment capabilities, and offer electrical isolation between shafts. Jaw couplings are widely used in light to medium-duty applications. 6. Oldham Couplings:Oldham couplings have three discs—two outer discs with slots and a central disc with a tongue that fits into the slots. They provide excellent angular misalignment compensation while maintaining constant velocity between shafts. Oldham couplings are commonly used in printing machines and conveyors. 7. Beam Couplings:Beam couplings are made from a single piece of flexible material with spiral cuts. They offer good misalignment compensation and torsional flexibility, making them suitable for precision equipment like encoders and servo motors. The choice of coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application, including torque, speed, misalignment compensation, environmental conditions, and space limitations. Each coupling type has its strengths and limitations, and selecting the right coupling is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability in the mechanical system. “` Best Practices for Installing a Shaft Coupling for Optimal PerformanceProper installation of a shaft coupling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure. Follow these best practices to install a shaft coupling correctly: 1. Shaft Alignment:Ensure that both the driving and driven shafts are properly aligned before installing the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and other connected components, reducing efficiency and causing premature wear. Use alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve accurate shaft alignment. 2. Cleanliness:Before installation, clean the shaft ends and the coupling bore thoroughly. Remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could interfere with the coupling’s fit or cause misalignment. 3. Lubrication:Apply the recommended lubricant to the coupling’s contact surfaces, such as the bore and shaft ends. Proper lubrication ensures smooth installation and reduces friction during operation. 4. Correct Fit:Ensure that the coupling is the correct size and type for the application. Use couplings with the appropriate torque and speed ratings to match the equipment’s requirements. 5. Fastening:Use the recommended fastening methods, such as set screws or keyways, to securely attach the coupling to the shafts. Make sure the fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation. 6. Spacer or Adapter:If required, use a spacer or adapter to properly position the coupling on the shafts and maintain the desired distance between the driving and driven components. 7. Avoid Shaft Damage:Be careful during installation to avoid damaging the shaft ends, especially when using set screws or other fastening methods. Shaft damage can lead to stress concentrations and eventual failure. 8. Check Runout:After installation, check the coupling’s runout using a dial indicator to ensure that it rotates smoothly and without wobbling. Excessive runout can indicate misalignment or improper fit. 9. Periodic Inspection:Regularly inspect the coupling and its components for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Perform routine maintenance as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent issues from worsening over time. 10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and guidelines. Different types of couplings may have specific installation requirements that need to be adhered to for optimal performance and safety. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your shaft coupling is installed correctly, maximizing its efficiency and reliability in your mechanical power transmission system. “` China Hot selling Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint CouplingProduct Description
Stainless Steel Coupling Gear Rigid Roller Chain Fluid Tyre Grid Jaw Spider HRC Nm Motor Flange Gear Pump Rubber Spline Shaft Flexible Universal Joint Coupling Product Description Main products Couplings can be divided into rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Coupling performance 1) Mobility. The movability of the coupling refers to the ability to compensate the relative displacement of 2 rotating components. Factors such as manufacturing and installation errors between connected components, temperature changes during operation and deformation under load all put CHINAMFG requirements for mobility. The movable performance compensates or alleviates the additional load between shafts, bearings, couplings and other components caused by the relative displacement between rotating components. How to select the appropriate coupling type The following items should be considered when selecting the coupling type. If you cannot determine the type, you can contact our professional engineer Related products
Company Profile
Our Equipments Main production equipment:
Machining equipments
Our Factory Company Profile /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
Understanding the Torque and Misalignment Capabilities of Shaft CouplingsShaft couplings play a critical role in transmitting torque and accommodating misalignment between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. Understanding their torque and misalignment capabilities is essential for selecting the right coupling for a specific application. Here’s an overview: Torque Transmission:The torque capacity of a shaft coupling refers to its ability to transmit rotational force from one shaft to another. It is typically specified in torque units, such as Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). The coupling’s torque capacity depends on its design, size, and material. When selecting a coupling, it’s crucial to ensure that its torque capacity meets or exceeds the torque requirements of the application. Overloading a coupling beyond its torque capacity can lead to premature failure or damage to the coupling and connected equipment. Misalignment Compensation:Shaft misalignment can occur due to various factors, including thermal expansion, manufacturing tolerances, or foundation settling. Misalignment puts additional stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially leading to increased wear and reduced efficiency. Shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignment:
The coupling’s misalignment capabilities are specified in terms of angular and axial misalignment values, usually in degrees or millimeters. Different coupling designs can accommodate varying degrees of misalignment, and the choice depends on the specific application and operating conditions. Flexible Couplings:Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric or jaw couplings, offer good misalignment compensation. They can handle a combination of angular, parallel, and axial misalignments. However, their torque capacity may be limited compared to rigid couplings. Rigid Couplings:Rigid couplings, such as clamp or sleeve couplings, have high torque transmission capabilities but offer minimal misalignment compensation. They are best suited for applications where shafts are well-aligned and precise torque transmission is critical. Torsional Stiffness:Another factor to consider is the coupling’s torsional stiffness, which determines how much torsional deflection or twist occurs under load. Some applications, like precision systems, may require couplings with high torsional stiffness to maintain accurate positioning and avoid torsional backlash. By understanding the torque and misalignment capabilities of shaft couplings, engineers can make informed decisions when selecting a coupling to ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance in their mechanical systems. “` How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft CouplingRegular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for: 1. Visible Damage:Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload. 2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point. 3. Increased Temperature:If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues. 4. Shaft Misalignment:Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components. 5. Excessive Backlash:If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components. 6. Lubrication Issues:Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear. 7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation. 8. Bolts and Fasteners:Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure. 9. Age and Service Life:Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure. 10. Abnormal Performance:Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues. If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely. “` How Does a Flexible Shaft Coupling Differ from a Rigid Shaft Coupling?Flexible shaft couplings and rigid shaft couplings are two distinct types of couplings, each designed to serve different purposes in mechanical power transmission. Here are the key differences between the two: 1. Flexibility:The most significant difference between flexible and rigid shaft couplings is their flexibility. Flexible couplings are designed with elements that can deform or flex to accommodate misalignments between the shafts. This flexibility allows for angular, parallel, and axial misalignments, making them suitable for applications where shafts are not perfectly aligned. In contrast, rigid couplings do not have this flexibility and require precise alignment between the shafts. 2. Misalignment Compensation:Flexible couplings excel in compensating for misalignments, making them ideal for applications with dynamic conditions or those prone to misalignment due to thermal expansion or vibrations. Rigid couplings, on the other hand, are used in applications where perfect alignment is critical to prevent vibration, wear, and premature failure. 3. Damping Properties:Flexible couplings, particularly those with elastomeric or flexible elements, offer damping properties, meaning they can absorb and reduce shocks and vibrations. This damping capability helps protect the connected equipment from damage and enhances system reliability. Rigid couplings lack this damping ability and can transmit shocks and vibrations directly between shafts. 4. Torque Transmission:Both flexible and rigid couplings are capable of transmitting torque from the driving shaft to the driven shaft. However, the torque transmission of flexible couplings can be limited compared to rigid couplings, especially in high-torque applications. 5. Types of Applications:Flexible couplings find applications in a wide range of industries, especially in situations where misalignment compensation, vibration damping, and shock absorption are essential. They are commonly used in conveyors, pumps, compressors, printing presses, and automation systems. Rigid couplings are used in precision machinery and applications that demand perfect alignment, such as high-speed spindles and certain types of precision equipment. 6. Installation:Flexible couplings are relatively easier to install due to their ability to accommodate misalignment. On the other hand, rigid couplings require careful alignment during installation to ensure proper functioning and prevent premature wear. The choice between a flexible and a rigid shaft coupling depends on the specific requirements of the application. If misalignment compensation, damping, and flexibility are critical, a flexible coupling is the preferred choice. If precision alignment and direct torque transmission are essential, a rigid coupling is more suitable. “` China Best Sales High Pressure Flexible Quick Universal Hose Stainless Steel Groove Shaft CouplingProduct Description
Product Name: Flexible Quick Universal Hose Connector Pipe Fitting Stainless Steel Groove Shaft Coupling Other Product
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Our Advantages 1. Rich manufacturing experience.
Company Profile
HangZhou Tontr Pipeline System Co., Ltd. is located in the beautiful coastal city of HangZhou. It is a professional national-level high-tech industry engaged in the design, development, manufacture and sales of high-pressure pipeline systems. Packing&Shipping FAQ Q1: Are you a manufacturer?
Certifications
How to Select the Right Shaft Coupling for Specific Torque and Speed RequirementsSelecting the appropriate shaft coupling involves considering the specific torque and speed requirements of the application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you choose the right coupling: 1. Determine Torque and Speed:Identify the torque and speed requirements of the application. Torque is the rotational force required to transmit power between the shafts, usually measured in Nm (Newton-meters) or lb-ft (pound-feet). Speed refers to the rotational speed of the shafts, typically measured in RPM (revolutions per minute). 2. Calculate Torque Capacity:Check the torque capacity of various shaft couplings. Manufacturers provide torque ratings for each coupling type and size. Ensure that the selected coupling has a torque capacity that exceeds the application’s torque requirements. 3. Consider Misalignment:If the application involves significant shaft misalignment due to thermal expansion, vibration, or other factors, consider flexible couplings with good misalignment compensation capabilities. Elastomeric or beam couplings are popular choices for such applications. 4. Assess Operating Speed:For high-speed applications, choose couplings with high rotational speed ratings to avoid resonance issues and potential coupling failure. High-speed couplings may have specialized designs, such as disk or diaphragm couplings. 5. Evaluate Environmental Conditions:If the coupling will operate in harsh environments with exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures, select couplings made from corrosion-resistant materials or with protective coatings. 6. Check Torsional Stiffness:In applications requiring precision motion control, consider couplings with high torsional stiffness to minimize torsional backlash and maintain accurate positioning. Bellows or Oldham couplings are examples of couplings with low torsional backlash. 7. Size and Space Constraints:Ensure that the selected coupling fits within the available space and aligns with the shaft dimensions. Be mindful of any installation limitations, especially in confined spaces or applications with limited radial clearance. 8. Consult Manufacturer’s Data:Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs and technical data sheets for detailed information on each coupling’s torque and speed ratings, misalignment capabilities, materials, and other relevant specifications. 9. Consider Cost and Maintenance:Compare the costs and maintenance requirements of different couplings. While some couplings may have higher upfront costs, they could offer longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in the long run. By following these steps and considering the specific torque and speed requirements of your application, you can select the right shaft coupling that will ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance for your mechanical system. “` How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft CouplingRegular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for: 1. Visible Damage:Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload. 2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point. 3. Increased Temperature:If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues. 4. Shaft Misalignment:Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components. 5. Excessive Backlash:If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components. 6. Lubrication Issues:Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear. 7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation. 8. Bolts and Fasteners:Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure. 9. Age and Service Life:Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure. 10. Abnormal Performance:Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues. If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China wholesaler CNC Customizable Forged Steel Flexible Jaw Tooth Shaft Gear CouplingsProduct Description
Ruika has been engaged in manufacturing of forgings, castings, heat treatment and CNC machining parts since 1999. The products materials have passed EN15714-3.1 certification, covering various grades of: low carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, ductile iron, aluminum alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy. The main processes are: free forging, die forging, rolling ring, high pressure casting, centrifugal casting, normalizing, quenching and tempering, solution treatment, aging treatment, carbonitriding, turning, milling, drilling, grinding, hobbing, high frequency quenching, galvanizing, chrome plating, anodizing, powder spraying and other processes. Rings and plates dimensions: Max 3000mm, shafts length: Max 12000mm, single piece weight: Max 16 Tons, at the same time we are good at terminal machining of complex products, dimension accuracy: Min 0.01mm, roughness: Min Ra0.6. Products can be strictly examined by chemical composition, tensile strength, yield strength, reduction of area, impact at low temperature, intergranular corrosion, hardness, metallographic, NDT, size, static balance etc performance parameter. Products are widely used in: aerospace, ships, trains, automobiles, engineering vehicles, chemical industry and petroleum refining, wellheads, x-mas tree equipment, mining machinery, food machinery, hydraulic and wind power generation, new energy equipment etc field. Welcome to send: PDF, IGS, STP and other format drawings, of course we could also make material judgment and size survey according to your samples. With more than 20 years of manufacturing experience and overseas sales team, we have achieved 100% customer satisfaction. The warranty period of products sold is 365 days. We look CZPT to your consultation and cooperation at any time and common prosperity development.
Specific Safety Precautions When Working with Shaft CouplingsWorking with shaft couplings involves handling rotating machinery and mechanical components. To ensure the safety of personnel and prevent accidents, specific safety precautions should be followed during installation, maintenance, and operation: 1. Lockout-Tagout (LOTO):Prior to any work on machinery involving couplings, implement a lockout-tagout procedure to isolate the equipment from its power source. This ensures that the machinery cannot be accidentally energized during maintenance or repair, protecting workers from potential hazards. 2. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety goggles, gloves, and appropriate clothing, when working with shaft couplings. PPE helps protect against potential hazards such as flying debris, sharp edges, or contact with moving parts. 3. Proper Training and Supervision:Only trained and authorized personnel should work with shaft couplings. Ensure that workers have the necessary knowledge and experience to handle the equipment safely. Adequate supervision may be required, especially for less-experienced personnel. 4. Inspection and Maintenance:Regularly inspect shaft couplings and associated components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Address any issues promptly to prevent equipment failure and potential accidents. 5. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:Adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for installation, operation, and maintenance of the specific coupling model. Improper use or deviation from recommended procedures may compromise safety and void warranties. 6. Avoid Overloading:Do not exceed the torque and speed limits specified by the coupling manufacturer. Overloading a coupling can lead to premature failure and pose safety risks to operators and nearby equipment. 7. Shaft Guards and Enclosures:Install appropriate guards and enclosures to prevent accidental contact with rotating shafts and couplings. These safety measures help reduce the risk of entanglement and injuries. 8. Zero Energy State:Ensure that all stored energy in the equipment, such as compressed air or hydraulic pressure, is released and the equipment is in a zero energy state before starting work. 9. Avoid Loose Clothing and Jewelry:Remove or secure loose clothing, jewelry, and other items that could get caught in moving parts. 10. Maintain a Clean Work Area:Keep the work area clean and free from clutter to avoid tripping hazards and facilitate safe movement around the machinery. By following these safety precautions, personnel can minimize the risks associated with working with shaft couplings and create a safer working environment for everyone involved. “` Explaining the Concept of Backlash and How It Affects Shaft Coupling PerformanceBacklash is the angular movement or play between the mating components of a mechanical system when the direction of motion is reversed. In the context of shaft couplings, backlash refers to the free rotational movement between the connected shafts before the coupling transmits torque from one shaft to the other. Backlash occurs in certain coupling designs that have features allowing relative movement between the coupling’s mating parts. Common coupling types that may exhibit some degree of backlash include elastomeric couplings (such as jaw couplings), gear couplings, and Oldham couplings. How Backlash Affects Shaft Coupling Performance:1. Loss of Precision: In applications requiring precise motion control, backlash can lead to inaccuracies and reduced positional accuracy. For example, in CNC machines or robotics, any rotational play due to backlash can result in positioning errors and decreased machining or movement precision. 2. Reversal Impact: When a reversing load is applied to a coupling, the presence of backlash can lead to a brief period of rotational play before the coupling re-engages, causing a momentary jolt or impact. This impact can lead to increased stress on the coupling and connected components, potentially reducing their lifespan. 3. Dynamic Response: Backlash can affect the dynamic response of the mechanical system. In systems requiring rapid acceleration or deceleration, the initial play due to backlash may create a delay in torque transmission, affecting the system’s responsiveness. 4. Noise and Vibration: Backlash can cause noise and vibration in the system, leading to increased wear and potential fatigue failure of components. 5. Misalignment Compensation: In some flexible coupling designs, a certain amount of backlash is intentionally incorporated to allow for misalignment compensation. While this is a beneficial feature, excessive backlash can compromise the coupling’s performance. Minimizing Backlash:Manufacturers often design couplings with specific features to minimize backlash. For instance, some gear couplings employ crowned gear teeth to reduce clearance, while elastomeric couplings may have preloaded elastomeric elements. Precision couplings like zero-backlash or torsionally rigid couplings are engineered to eliminate or minimize backlash for applications requiring high accuracy and responsiveness. When selecting a coupling, it’s essential to consider the application’s specific requirements regarding precision, speed, reversing loads, and misalignment compensation, as these factors will determine the acceptable level of backlash for optimal performance. “` Diagnosing and Fixing Common Issues with Shaft CouplingsRegular inspection and maintenance of shaft couplings are essential to detect and address common issues that may arise during operation. Here are steps to diagnose and fix some common coupling problems: 1. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:If you notice unusual noise or excessive vibration during equipment operation, it may indicate misalignment, wear, or damage in the coupling. Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks or deformations, and inspect the coupling for proper alignment. Diagnosis:Use a vibration analysis tool to measure the vibration levels and identify the frequency of the abnormal vibrations. This can help pinpoint the source of the problem. Fix:If misalignment is the cause, adjust the coupling to achieve proper alignment between the shafts. Replace any damaged or worn coupling components, such as spiders or elastomeric inserts, as needed. 2. Excessive Heat:Feeling excessive heat on the coupling during operation can indicate friction, improper lubrication, or overload conditions. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling and surrounding components for signs of rubbing, lack of lubrication, or overloading. Fix:Ensure proper lubrication of the coupling, and check for any interference between the coupling and adjacent parts. Address any overloading issues by adjusting the equipment load or using a coupling with a higher torque capacity. 3. Shaft Movement:If you observe axial or radial movement in the connected shafts, it may indicate wear or improper installation of the coupling. Diagnosis:Check the coupling’s set screws, keyways, or other fastening methods to ensure they are secure and not causing the shaft movement. Fix:If the coupling is worn or damaged, replace it with a new one. Ensure proper installation and use appropriate fastening methods to secure the coupling to the shafts. 4. Sheared Shear Pin:In shear pin couplings, a sheared shear pin indicates overloading or shock loads that exceeded the coupling’s torque capacity. Diagnosis:Inspect the shear pin for damage or breakage. Fix:Replace the sheared shear pin with a new one of the correct specifications. Address any overloading issues or adjust the equipment to prevent future shearing. 5. Coupling Wear:Regular wear is normal for couplings, but excessive wear may lead to decreased performance and increased misalignment. Diagnosis:Inspect the coupling components for signs of wear, such as worn elastomeric elements or damaged teeth. Fix:Replace the worn or damaged components with new ones of the appropriate specifications. Remember, regular maintenance and periodic inspection are key to diagnosing issues early and preventing severe problems. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance and replacement schedules to ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the shaft coupling. “` China manufacturer Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for CentaflexProduct Description
Original Excavator Parts Coupling CF-a Series Rubber Flexible Torsionally Steel Universal Shaft Coupling for Centafle Product Display:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||